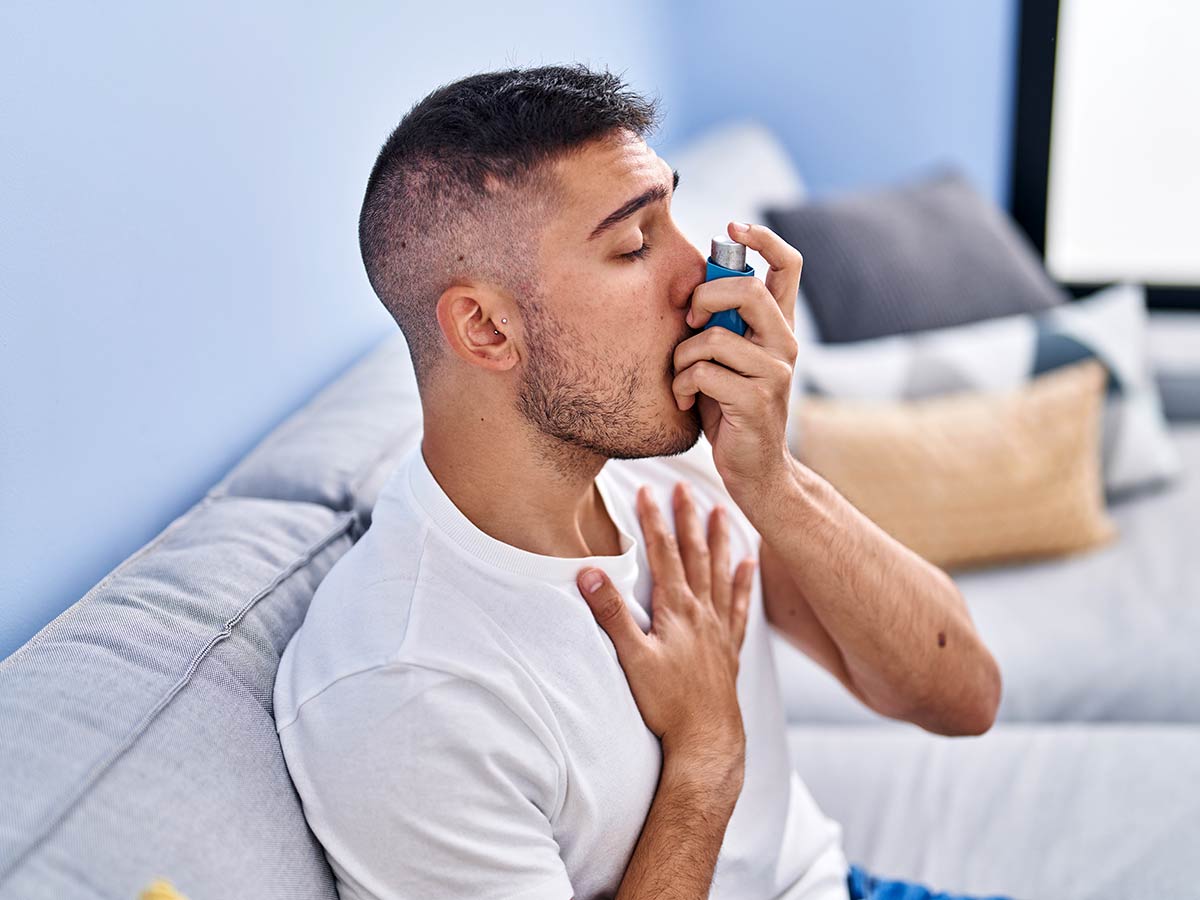
Asthma is the most prevalent chronic illness in children and is a serious noncommunicable disease (NCD) that affects both children and adults.
Asthma symptoms, which can include any combination of coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and tightness in the chest, are brought on by inflammation and restriction of the tiny airways in the lungs.
Inhalation Therapy For Asthma Treatment
Inhalation therapy is a crucial part of managing asthma. However, individuals with asthma are frequently unable to accept or adhere to the inhalation therapy that their doctor has prescribed because of misunderstandings regarding the medication. In fact, the GAN study found that only 9% of people who have been diagnosed with asthma receive the essential ICS (inhaled corticosteroids) therapy.
Why Use Inhalers?
The mainstay of controlling chronic respiratory disorders like asthma is inhalation therapy. This is a result of its exact dosage, delivery, and duration of alleviation. When compared to oral treatments, inhalation devices administer the medication directly to the airways and lungs, requiring smaller dosages and lowering the chance of side effects. Inhalers may also include fast-acting drugs that, when needed, offer relief right away. This is particularly crucial for people who have been diagnosed with asthma because an asthma attack can be very serious. In these circumstances, a quick-acting asthma inhaler can be very helpful and make a big difference.
Also, Read 8 Most Effective Medicinal Herb
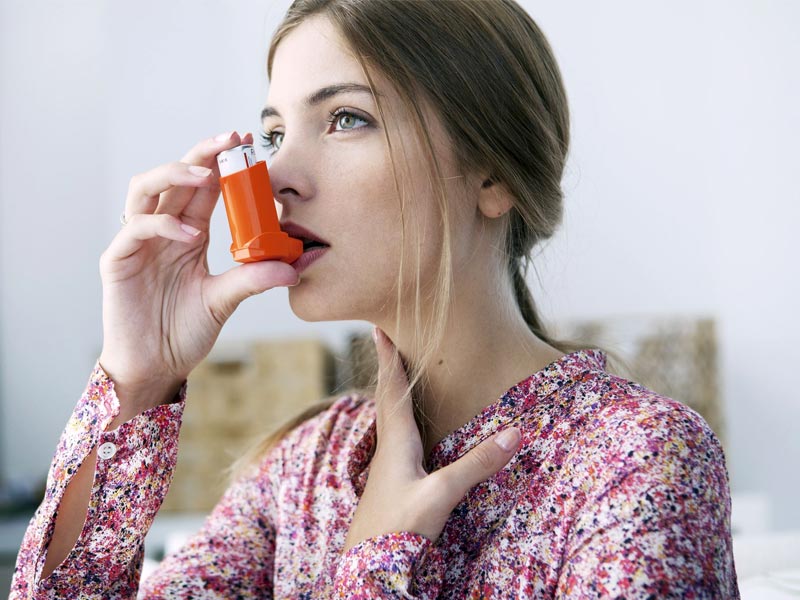

Utilizing The Proper Inhaler
Choosing the right inhaler and administering it correctly will help you get the medication you need to control your symptoms, stop exacerbations, or get quick relief from an asthma attack. If you have asthma, for example, your doctor may give inhalers as a long-term therapy option. If you simply have a manageable but serious acute infection, like pneumonia, however, your doctor may only prescribe an inhaler.
Based on the severity and features of your illness, doctors may recommend one of several types of asthma inhalers to help control your symptoms. Inhalers that are among the most popular kinds are as follows:
Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers (pMDIs):
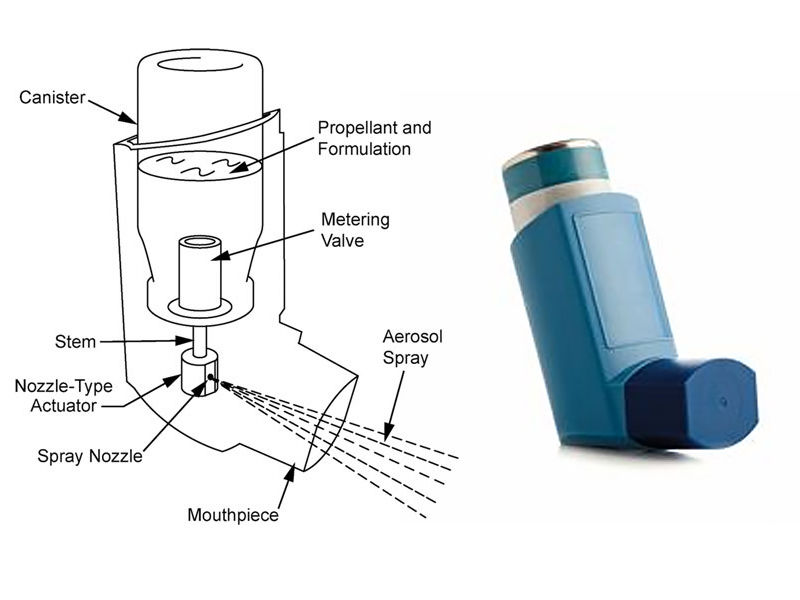
The most popular type of inhaler is called a pressurized metered dose inhaler (pMDI), which consists of a pressurized canister containing medication combined with aerosol propellants that are released as a spray when a button is pressed. For those who are younger or older, using a spacer with an inhaler may make it easier to inhale the entire amount. The spacer holds the drug in a tube between the inhaler and the mouth after it has been administered.
Dry Powder Inhalers (DPIs):
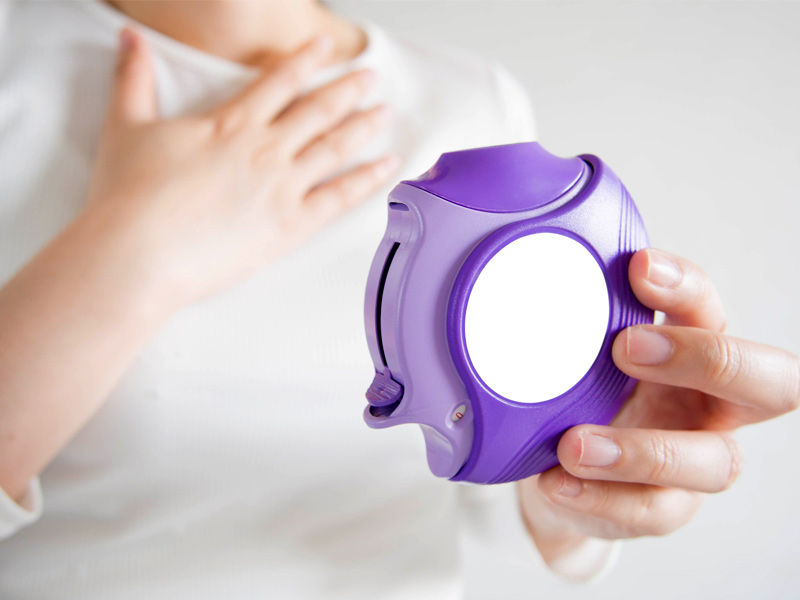

Dry powder inhalers (DPIs) release medication in the form of dry powder when the user inhales deeply and quickly, as opposed to utilizing a propellant to force it out. DPIs can be found in single-dose devices that need to be filled with a fresh capsule each time or multi-dose devices with a huge capacity, depending on the dosage required.
Breath-Actuated Inhalers (BAIs):
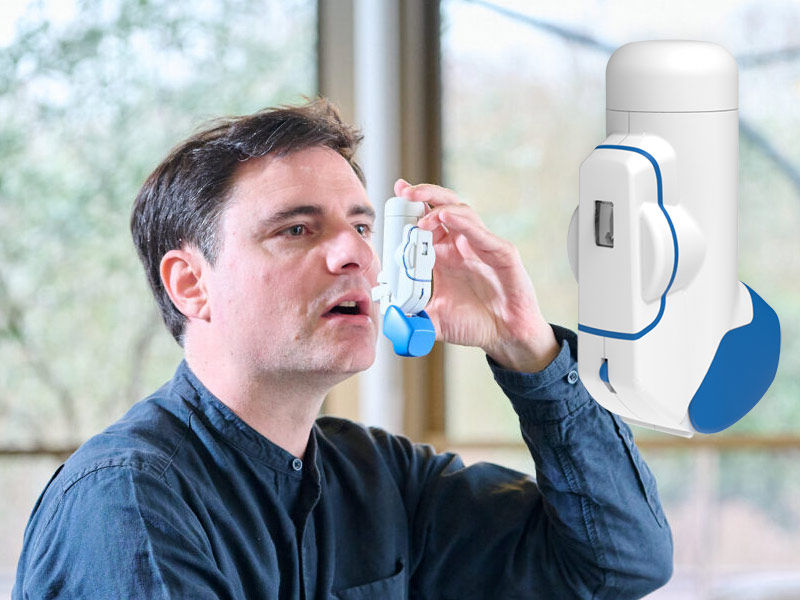

Breath-actuated metered-dose inhalers solve the coordination difficulty of conventional pressurized metered-dose inhalers while providing the advantages of compactness, portability, and multiple doses. It is simpler to administer the medication in hospitals and by patients themselves because it is released upon inhalation. Children and the elderly, who may not have a powerful enough inhalation to activate it, may not be a good candidate for this type of inhaler.
Why Technique Is Important
For an inhaler to work well, proper usage is essential. Because technique varies from device to device, patients should ask their doctor for advice to learn the right method. Incorrect inhaler use can lead to insufficient disease control, an increase in ER visits, and a higher risk of hospitalization. Additionally, improper administration hinders the drug from getting to the lungs and airways, which results in therapy failure.

It’s also critical to mark both the controller and reliever inhalers to prevent any mistakes between the devices and to keep track of the remaining doses. The inhaler must be regularly cleaned to prevent the buildup of debris, which can exacerbate lung disease and reduce the efficacy of treatment.
It is advisable to get a new inhaler when the dose counter turns from green to red, signifying fewer doses. These suggestions will make using inhalers simple and make long-term asthma management less difficult.

























