One excellent source of vitamin D for humans is the sun. However, it is still possible to receive insufficient amounts of vitamin D, which can have detrimental effects on health. A vitamin D deficiency can cause a loss of bone density, which can exacerbate osteoporosis and fractures (broken bones), according to the National Library of Medicine. In addition, severe vitamin D deficiency can cause other illnesses. Additionally, vitamin D’s potential links to a number of illnesses, such as diabetes, hypertension, cancer, and autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, are being investigated by researchers.
reasons to think about increasing your outdoor time if your doctor says you don’t have enough vitamin D.
Obesity

A 2015 meta-analysis published in Obesity Reviews found that individuals who are obese—men, women, and children—are 35% more likely than non-obese individuals to be vitamin D deficient, and overweight individuals are 24% more likely to be D deficient. As fat cells retain vitamins and release them inefficiently, the buildup of vitamin D in adipose tissue may account for the low blood levels of vitamin D in obese individuals, according to a 2019 review published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Translation: It’s possible that obesity exacerbates vitamin D deficiency.
Diabetes

A 2015 Spanish study that was published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that individuals with diabetes or prediabetes had lower vitamin D levels than people with normal blood sugar levels. The connection worked for people with a range of BMIs. Indeed, individuals with diabetes or prediabetes who were lean or severely obese had significantly lower D than those who were not diabetics. The authors of the study hypothesise that obesity and vitamin D deficiency “interact synergistically” to raise the risk of diabetes and other metabolic diseases.
Heart Conditions
It is well known that vitamin D deficiency and heart disease are related. A 2022 study that was published in the European Heart Journal revealed evidence linking vitamin D deficiency to elevated blood pressure and an increased risk of heart disease.
Experts assert that there isn’t any proof, though, that lower cardiovascular risk and increased vitamin D levels are related. A meta-analysis on vitamin D supplementation and over 83, 000 participants was published in JAMA Cardiology in 2019. Researchers in the study discovered no correlation between vitamin D supplementation and lower risks of major adverse cardiovascular events, myocardial infarction, stroke, or mortality from cardiovascular disease.
Lupus
According to the Lupus Foundation of America, vitamin D deficiency is frequently linked to lupus, a chronic inflammatory disease in which the body’s immune system attacks its own organs and tissues. This is partly because patients with lupus are often advised to avoid the sun, which provides 90% of our vitamin D, and may be prescribed corticosteroids, which are also associated with low vitamin D levels.
PMS
In a 2017 study published in Gynaecological Endocrinology, high dose vitamin D supplementation was found to reduce the prevalence of PMS and dysmenorrhea (severe and frequent menstrual cramps and pain during your period, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine). Additionally, vitamin D improved both the psychological and physical symptoms associated with PMS.

The first line of treatment for PMS symptoms is still non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen and naproxen, but vitamin D supplements are seen as a promising substitute by researchers.
Also read: 5 Vegetables that you should never consume raw
Hair Loss and Alopecia
A 2013 study published in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology found that women with female pattern hair loss had significantly lower levels of vitamin D than those without hair loss. The vitamin facilitates the transition of hair from the resting to the growing phases and is essential for hair cycling.
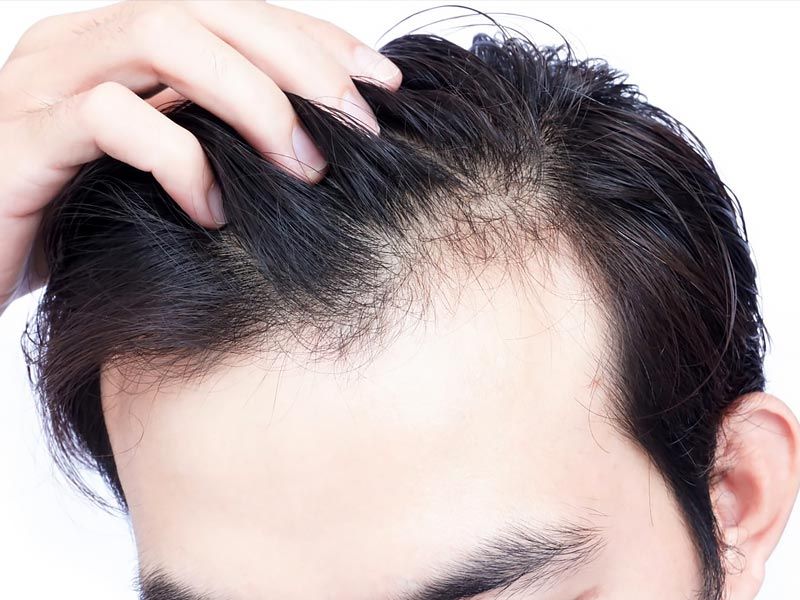

In a 2014 study published in the British Journal of Dermatology, Turkish researchers discovered that patients with alopecia areata, an autoimmune disease that attacks follicles and can cause hair loss throughout the body, had significantly lower levels of 25-hydroxy vitamin D than people without the condition. Researchers also found that the severity of the disease increased with decreasing D levels.

























