A liver sickness that can happen in late pregnancy is called intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, or simply cholestasis of pregnancy. Severe itching is brought on by the condition, but there is no rash. Although it can happen on other parts of the body, itching usually occurs on the hands and feet.
Pregnancy-related cholestasis can be extremely uncomfortable. However, the possible complications are more concerning, particularly for your infant. Due to the possibility of difficulties, your healthcare provider may advise an early delivery at 37 weeks.
Causes
It’s unclear what specifically causes cholestasis during pregnancy. Bile flow is decreased or ceases during cholestasis. The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid that aids in the breakdown of fats. Bile accumulates in the liver rather than moving from it to the small intestine. Bile acids consequently eventually find their way into the bloodstream. Pregnancy-related cholestasis symptoms and complications seem to be brought on by elevated bile acid levels.
Genetics, the environment, and pregnancy hormones could all be involved.
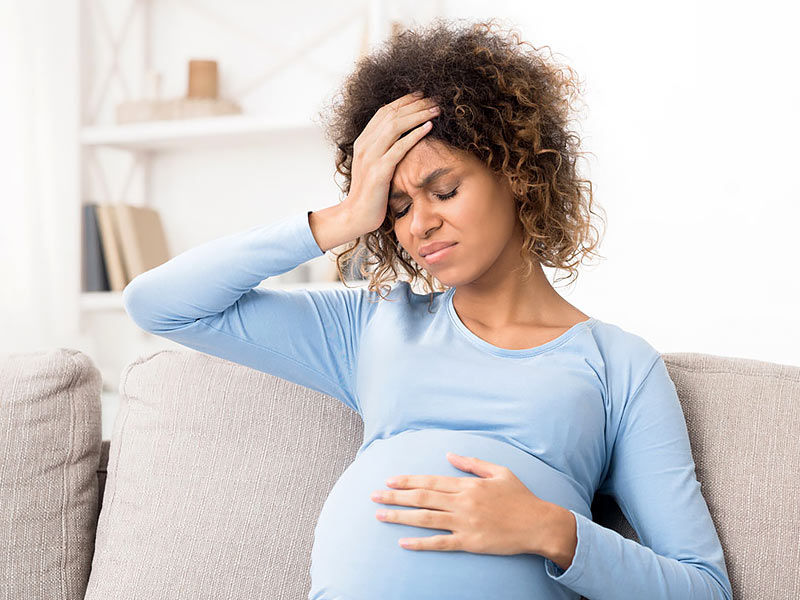

hormones. The closer your due date is, the more pregnant you feel. Bile flow may be slowed as a result.
DNA. The illness can occasionally run in families. Pregnancy-related cholestasis may be associated with specific gene alterations that have been discovered.
surroundings. Risk varies by region and season, though the precise environmental factors are unknown.
Risk factors
The following are some variables that could raise your chance of getting cholestasis during pregnancy:
pregnancy-related cholestasis in oneself or one’s family
Past medical history of liver disorders or damage, such as gallstones and hepatitis C
having several children while pregnant
pregnancy at a later age, like 35 or beyond
Your chances of getting cholestasis during a subsequent pregnancy are increased if you have a history of the condition. In roughly 60% to 70% of females, it reoccurs. We refer to this as a recurrence. The chance of a recurrence in severe cases might reach 90%.
Also read: 5 Foods with More Iron Than Spinach
Complications
Elevated blood levels of bile acid seem to be the cause of complications resulting from pregnancy-related cholestasis. While complications in the mother are possible, the developing child is particularly vulnerable.
The illness may momentarily alter a mother’s body’s ability to absorb fat. Reduced levels of blood clotting factors dependent on vitamin K may be the consequence of poor fat absorption. However, this is not a common issue. Although rare, liver issues in the future are possible.