Intermittent fasting (IF) is one of the world’s most common health and fitness phenomena right now. It is being used to help people lose weight, improve their fitness, and ease their lives. Many tests have shown that it has powerful effects on the body which brain and can also help you live longer. This is the definitive intermittent fasting beginner’s guide.
What Exactly Is Intermittent Fasting?
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a form of eating pattern that alternates between fasting and eating times. It does not define which foods to consume but rather when to eat them. In this regard, it is more aptly described as an eating habit rather than a diet in the traditional context.
Popular intermittent fasting strategies include regular 16-hour fasts or twice-weekly 24-hour fasts. Fasting has been practiced since the dawn of time. There were no stores, refrigerators, or food available all year for ancient hunter-gatherers. They sometimes couldn’t find something to eat. As a result, humans adapted to be able to survive for long periods without food. In reality, fasting on occasion is more natural than consuming 3–4 (or more) meals a day. Fasting is also practiced for religious or spiritual purposes in Buddhism, Jainism, and Hinduism.
Methods of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting may be done in various forms, including dividing the day or week into feeding and fasting times. You eat very little or none at all during the fasting times.

The below are the most often used methods:
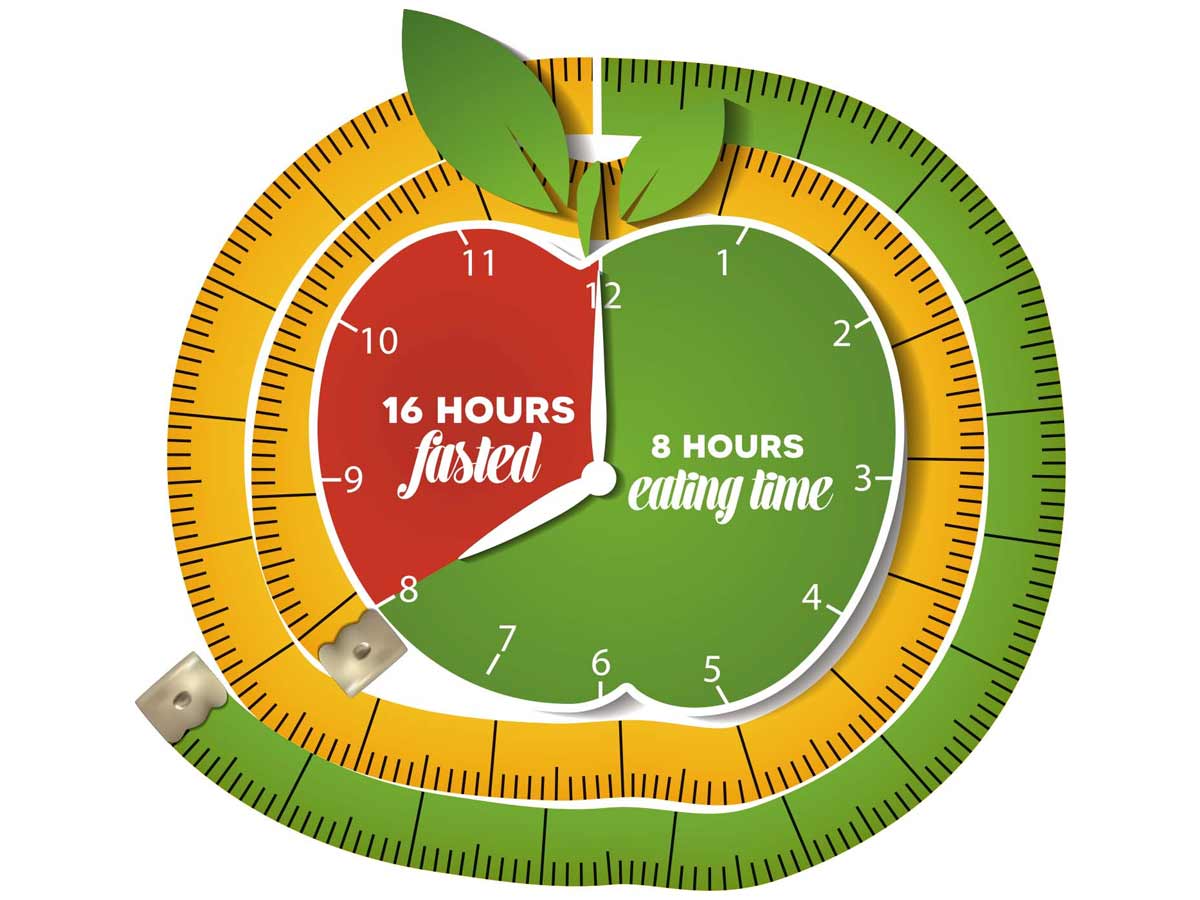
- The 16/8 rule: It is also known as the Leangains protocol. It entails missing breakfast and limiting the everyday mealtime to 8 hours, such as 1–9 p.m. You then fast for 16 hours in between.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: This means fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week, such as not feeding on dinner one day to dinner the next.
- The 5:2 diet: On two non-consecutive days of the week, you consume 500–600 calories but eat regularly on the remaining five.
These strategies can result in weight loss by lowering the calorie consumption, as long as you do not compensate by consuming any more during the eating hours. Many people believe that the 16/8 approach is the simplest, more sustainable, and easiest to follow. That is perhaps the most widely used.
Also Read, Pumpkin Seeds: Your very own Super Food
What It Does to Your Cells and Hormones
Several things happen in your body on the cellular and molecular levels as you hard. Your body, for example, changes hormone levels to make retained body fat more available. Your cells also begin critical repair processes and alter gene expression.
Here are some of the physiological changes that occur when you fast:
- HGH (Human Growth Hormone): Development hormone levels spike, growing up to fivefold. This has several advantages, including weight loss and muscle gain.
- Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin sensitivity increases and insulin levels fall significantly. Lower insulin levels increase the accessibility of retained body fat.
- Cellular repair: When you fast, your cells begin to repair themselves. This involves autophagy, in which cells eat and eliminate old and inactive proteins that accumulate within cells.
- Gene expression: There are variations in the action of genes associated with survival and disease resistance.
The health effects of intermittent fasting are improvements in hormone levels, cell structure, and gene expression.
A Very Effective Weight Loss Tool
The most popular cause for people to attempt intermittent fasting is to lose weight. Intermittent fasting, by forcing yourself to consume fewer meals, will result in an immediate decrease in calorie consumption.
Furthermore, intermittent fasting alters hormone levels, which aids in weight loss. It raises the fat-burning hormone norepinephrine release, lowers insulin, and raises growth hormone levels (noradrenaline). Because of these hormonal shifts, fasting for a short period may increase your metabolic rate by 3.6–14 percent.

Intermittent fasting causes weight reduction by shifting all aspects of the calorie scale by consuming fewer calories and burning additional calories. According to research, intermittent fasting can be a very effective weight-loss technique.
According to a 2014 review article, this eating pattern will result in 3–8 percent weight loss over 3–24 weeks, which is a substantial amount compared to other weight loss studies. According to the same report, people have lost 4–7 percent of their waist circumference, showing a substantial loss of unhealthy belly fat that builds up around the organs and induces illness.
Another research found intermittent fasting results in less muscle weakness than the more traditional form of sustained calorie restriction. Bear in mind, though, that the key explanation for its popularity is that intermittent fasting allows you to consume fewer calories overall. If you drink and overeat through your feeding hours, you will not lose much weight. Bear in mind, though, that the key explanation for its popularity is that intermittent fasting allows you to consume fewer calories overall. If you drink and overeat through your feeding hours, you will not lose much weight.
Health Benefits
Much research on intermittent fasting has been conducted in both animals and humans. These tests have demonstrated that it can have significant benefits for weight loss and overall body and brain wellbeing. It could also make you live a longer life.

The below are the primary health effects of extended fasting:
- Lose weight: As previously said, intermittent fasting will help you shed weight and belly fat without having to eat calories intentionally.
- Insulin resistance: Intermittent fasting can improve insulin resistance by reducing blood sugar by 3–6% and fasting insulin levels by 20–31%, potentially protecting against type 2 diabetes.
- Inflammation: Some reports suggest decreases in inflammation markers, which are a primary driver of many chronic diseases.
- Intermittent fasting can improve heart health by lowering “bad” LDL cholesterol, blood triglycerides, inflammatory markers, blood sugar, and insulin resistance, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
- Cancer prevention: Animal studies indicate that prolonged fasting can help prevent cancer.
- Intermittent fasting boosts the brain hormone BDNF and may help in the development of new nerve cells. It can also help to prevent Alzheimer’s disease.
- Intermittent fasting has been shown to increase lifespan in rats. Fasted rats lived 36–83 percent longer, according to studies.
Remember that the research is still in its early stages. Many of the experiments were limited, short-term, or animal-based. Many questions remain unanswered in high-quality human research.
Makes living a Healthy Lifestyle Easier
Eating healthy is easy, but it can be very difficult to sustain. One of the most significant barriers is the time and effort taken to schedule and prepare nutritious meals. Intermittent fasting will make life easier, so you don’t have to prepare, cook, or clean up after as many meals as you used to.
As a result, intermittent fasting is very common among the life-hacking crowd. It boosts your fitness while also simplifying your life.
Who Should Take Precautions Or Avoid It?
Intermittent fasting is not suitable for anyone. Suppose you are underweight or have a history of eating disorders. In that case, you should not fast without first consulting with a doctor.
In these circumstances, it can be very dangerous.
Is it appropriate for women to fast?

Any research suggests that intermittent fasting might not be as helpful to women as it is to men. One research, for example, found that it increased insulin sensitivity in men but worsened blood sugar regulation in women. While human research on this subject is lacking, studies in rats have shown that intermittent fasting can cause female rats to become emaciated, masculinized, infertile, and skip their cycles.
There have been some anecdotal accounts of people whose menstrual periods ended after they began doing IF and returned to usual after continuing their prior eating routine. Women should exercise caution when it comes to intermittent fasting for these reasons. They should meet separate rules, such as easing into the profession and discontinuing quickly if they have any complications, such as amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
If you are having fertility problems and/or struggling to adapt, you should postpone intermittent fasting for the time being. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, this eating habit is probably not a good one.
Side Effects and Safety
The most common side effect of intermittent fasting is hunger. You can still feel tired, and the brain may not do as well as it used to. This will only be temporary since the body will need time to adjust to the new meal plan.
If you have a medical condition, talk to the doctor before attempting intermittent fasting.
-
This is especially important if you suffer from diabetes.
-
Had issues with blood sugar control.
-
Get a low blood pressure reading.
-
Take your medications.
-
You are underweight.
-
Have an eating disorder experience.
-
You are a female who is attempting to conceive.
-
You have a diagnosis of amenorrhea.
-
Are you pregnant or breastfeeding?