Rapid eye movement (REM for sleep) Sleep is one of the four phases of the sleep cycle that the brain goes through. This stage of the sleep cycle normally occurs about 90 minutes after a person first falls asleep. It is characterized by many physiological changes such as muscle relaxation, eye movement, quicker respiration, and greater brain activity.
REM for Sleep Signs
The brain and body undergo several changes that are typical of this stage of sleep. The following are some significant indicators of REM for sleep:
- Temperature fluctuations in the body
- twitching of the body, notably the face, arms, and legs
- Increased blood pressure
- Increased blood pressure
- Heart rate is increasing.
- Increased oxygen consumption by the brain
- Quick eye movements
- Breathing that is rapid and erratic
- Arousal sexually
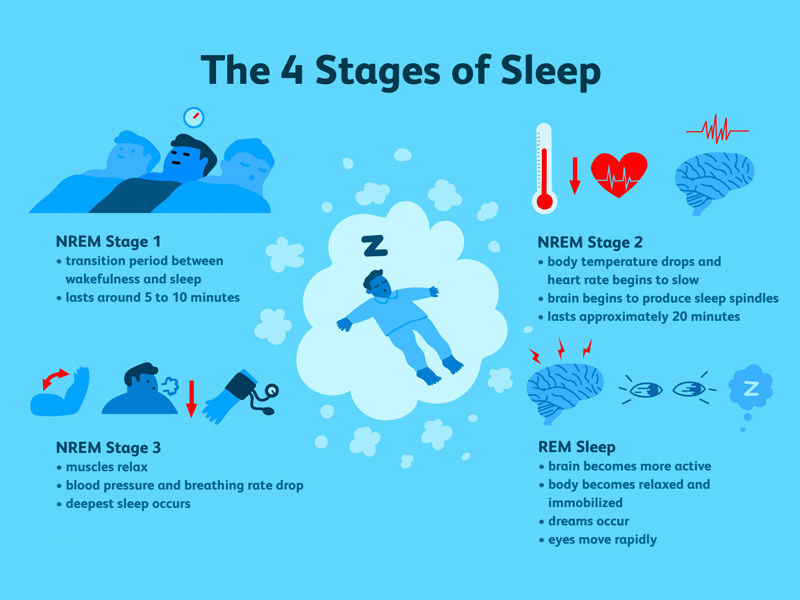
Stages of Sleep:
Stage 1
During stage 1, you alternate between being awake and sleeping. This is a brief NREM sleep that does not endure long. As you enter stage 2, you may begin to relax and dream, but you may also twitch.
Stage 2
Stage 2 of the sleep cycle is still a light sleep, but it gradually becomes a deeper sleep. Your heartbeat and breathing rate slow, and your muscles relax. The temperature of your body reduces, and your brain waves slow down.
Stages 3
Stage 3 ushers in a deep sleep, and stage 4 ushers in the deepest slumber. Deep sleep causes your respiration, heartbeat, body temperature, and brain waves to slow down. Your muscles are completely relaxed, and you are quite difficult to rouse.
Stage 4
Stage 4 is regarded as the healing stage because it is during this stage that tissue development and repair occur, vital hormones are released to accomplish their tasks, and cellular energy is recovered.
Also Read, 6 Habits That Might Be Affecting Your Sleep
REM (rapid eye movement) sleep
The first REM for sleep cycle of the night occurs approximately 90 minutes after you fall asleep and repeats every 90 minutes. Your eyes move fast beneath your eyelids, and your brainwaves resemble those of a person who is awake. Your heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate all increase to near-waking levels.
REM sleep, also known as stage 5, is when you are most likely to dream.
During this stage, your arms and legs become briefly paralyzed to prevent you from physically acting out your dreams.
What is the Importance of REM Sleep?
REM for sleep is vital for brain development and other activities such as mood, dreaming, and memory.
Dreams

Dreams occur or start during the rapid eye movement (REM) phase/stages of sleep. You dream for two hours on a typical night, which is broken up by the sleep cycle. Researchers do not fully understand why we sleep. They are aware that babies dream and that depriving mice of REM for sleep significantly reduces their lifespan. Other mammals and birds have REM sleep stages, but cold-blooded species like turtles, lizards, and fish do not.
Dreams can arise during any sleep phase, but those that come during REM for sleep are the most common and vivid.
Brain development research
According to brain development research, REM sleep plays a vital function in developing the central nervous system (CNS) throughout infancy. The high levels of activity in the brain during this sleep period may aid in developing and strengthening neural connections.
Memory

Dreams could be one way for the brain to consolidate memories. The dream time could be a time when the brain can rearrange and analyze the events of the day and relate new experiences to older ones. Because the body is shut down, the brain can do this without being interrupted by additional input or risking the body “playing out” the day’s memories.
According to some studies, dreams are more like background “noise” that is understood and arranged. According to the activation-synthesis theory, dreams are simply the brain’s attempt to make sense of random impulses during sleep.
Some people have a greater degree of control over their dreams than others. The last thoughts before going to bed for these folks may impact the content of a dream.
Difficulties
REM for sleep is critical for a variety of tasks, including learning and memory. Interruptions to REM sleep can occasionally cause issues. As a result, a lack of REM for sleep has been related to several health issues, including the following.
Reduced REM sleep is connected with changes in leptin levels and may be linked to increased appetite and weight.
Memory Consolidation
The pons also transmits impulses to the cerebral cortex via the thalamus (a filter and relay for sensory information and motor control function deep in the brain). The cerebral cortex is the area of the brain responsible for information processing (learning, thinking, and organizing).
The brain areas that are “switched on” during REM for sleep appear to aid in learning and remember. Infants spend over half of their sleep time in REM sleep (compared to 20% for adults), which may be explained by the great amount of learning throughout infancy.
When people are taught new abilities and subsequently deprived of REM for sleep, they frequently forget what they were taught.
Movement
REM sleep typically follows a period of deep sleep known as stage 3 sleep. The pons, a brain region where REM for sleep impulses originate, block signals to the spinal cord. As a result, the body remains immobile throughout REM sleep.
People will act out their fantasies if the pons does not shut down the spinal cord’s messages. This can be dangerous since acting out dreams without sensory input can result in accidents and bodily harm, such as running into walls and falling downstairs. This illness, known as REM sleep behavior disorder, is uncommon and distinct from more common sleepwalking.
Also Read, Did you know that sleep care is the new self-care?
Suggestions for Promoting Healthy REM Sleep
Maintain a Sleep Schedule
Every night, go to bed at the same time and wake up at the same time. Following a sleep routine will help you receive more quality sleep, including REM for sleep, each night.

Keep an eye on your alcohol consumption.
Before going to bed, limit your alcohol consumption. Even moderate alcohol use in the evening has been shown in studies to interfere with REM sleep. Light alcohol consumption did not appear to have the same effect. In contrast, moderate to heavy consumption postponed the commencement of REM sleep and resulted in fewer REM sleep phases during the night.
Keep Your Dreams in Mind
You can improve your capacity to recall your dreams by keeping a diary near your bed and taking notes of everything you remember about them when you first wake up. Your ability to remember your dreams will increase after a few weeks.
Some claim to have lucid dreams, which are dreams in which they can participate and modify the dream as it unfolds. A variety of approaches can induce lucid dreaming, albeit little study has been conducted on the subject.
If you or a loved one is suffering from a sleep disturbance, call the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 for local support and treatment options.

























