Human resource management (HRM) is hiring people, training them, rewarding them, setting policies for them, and devising retention tactics. HRM as a field has evolved significantly over the previous two decades, making it an even more vital position in today’s enterprises. HRM used to involve processing payroll, sending birthday gifts to staff, organizing company outings, and ensuring forms were completely filled out. In other words, more of an administrative duty than a strategic position critical to the organization’s success.
People are critical to the success of any company. Employee performance can be a burden or an advantage to a firm. As an HR professional, you will play a critical part in your company’s success. Human Resource Management (HRM) is critical for all sizes of enterprises. We shall go over the principles of Human Resource Management in this essay.
What is Human Resource Management?
Human resource management is the organizational function in charge of all concerns concerning people in a company. This includes, but is not limited to, remuneration, recruitment, selection, hiring, performance management, organizational development, safety, wellness, benefits, employee motivation, communication, policy administration, and training. Human resource management is also a complete and systematic approach to managing people and the workplace culture and environment. When done correctly, it allows employees to contribute effectively and productively to the overall corporate direction and achievement of their goals and objectives.
Members of the department supply the information, tools, training, administrative services, coaching, legal and management counsel, and talent management oversight that the rest of the business requires to function successfully.
7 Fundamentals that HR must consider
- Recruitment & selection
- Performance management
- Learning & development
- Succession planning
- Compensation and benefits
- Human Resources Information Systems
- HR data and analytics
1. Recruitment and Selection
Attracting and maintaining the best personnel in the industry is a top priority for many firms. HR managers play a crucial part in this. They help shape the company’s future by monitoring the recruitment and hiring processes. To begin, HR may collaborate with a department manager or supervisor to learn about a vacant position, including its needs and ideal candidate characteristics. The HR department can then devise a recruitment plan. This could include establishing internal and external job postings, evaluating resumes and other application materials from prospective applicants, and performing first interviews. HR may also be in charge of conducting professional reference checks and background checks to ensure candidates can work for the company.
2. Performance Management

Performance management becomes critical after staff is on board. The second HR fundamental is performance management. It entails assisting employees in being their best selves, hence increasing their bottom line.
Employees typically have a list of obligations that they must fulfill. Performance management is a structure that allows employees to receive feedback on their performance to achieve their peak performance.
Typically, businesses use a yearly performance management cycle that includes planning, monitoring, reviewing, and rewarding employee performance. The output of this approach allows personnel to be classified as high vs. low achievers and high vs. low potentials.
Successful performance management is a joint responsibility between HR and management. The direct manager typically takes the lead, and HR providing support. It is critical to have good performance management. Employees that are fully empowered boost a company’s efficiency, sustainability, and profit margin.
3. Learning and Development

People result from their life experiences, the place and era in which they grow up, and various cultural influences. Learning and development in human resources ensure that personnel adapts to changes in procedures, technology, and societal or legal upheavals.
Employees can reskill and upskill with the support of learning and development. HR is in charge of Learning & Development (L&D), and strong policies can be very beneficial in moving the firm closer to its long-term goals.
Also Read, How is artificial intelligence saving humans?
4. Succession Planning

Succession planning is the practice of preparing for the possibility of important personnel departing the firm. If, for example, a critical senior manager leaves his or her position, having a replacement ready will ensure continuity. It can save the organization a large amount of money.
Performance ratings and L&D initiatives are frequently used in succession planning. As a result, a talent pipeline is formed. This is a pool of qualified people ready to fill (senior) positions if someone leaves. Building and developing this pipeline is critical to effective people management.
5. Compensation and benefits

Compensation and benefits are another HR fundamental. Fair play is essential for inspiring and retaining employees. Ensure justice and fairness in pay is one of the fundamentals of human resource management.
Making the correct salary offer is an important component of attracting the top people. This must be balanced with the company’s budget and profit margins. HR should keep track of compensation rises and establish meritocracies. On occasion, HR may conduct a compensation audit.
Compensation is divided into two parts: main compensation and secondary compensation. Primary compensation consists of money received directly for employment, usually a monthly wage and sometimes performance-based pay. Non-monetary rewards are all examples of secondary advantages. This can include more vacation time, flexible working hours, daycare, pensions, a company car and laptop, and many other benefits. The idea here is to motivate people by rewarding them in creative ways.
6. Human Resource Information System
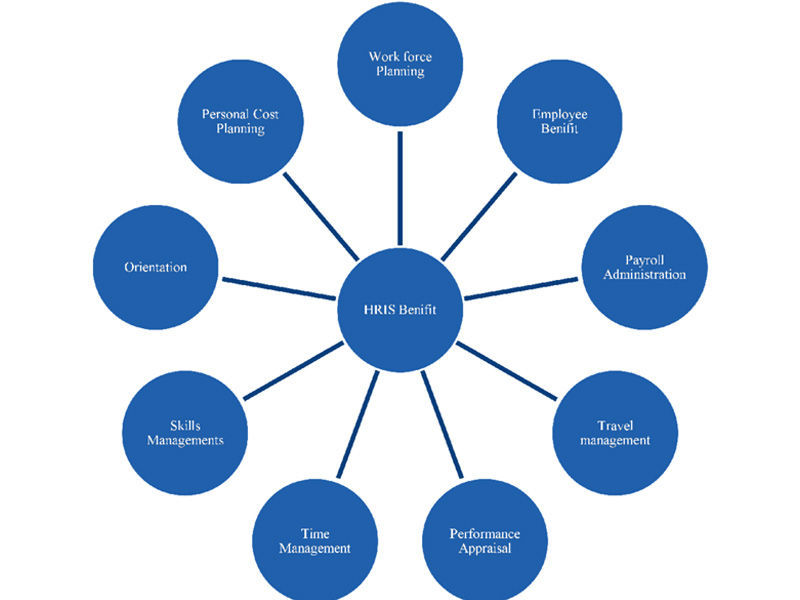
The last two HR fundamentals are not HR practices but rather tools for doing HR better. The Human Resource Information System, or HRIS, is the first. All of the pillars mentioned above are supported by an HRIS. HR professionals, for example, frequently utilize an Applicant Tracking System, or ATS, to keep track of applications and employees during recruiting and selection.
A performance management system is used to track individual goals and assign performance ratings for performance management.
A Learning Management System (LMS) is utilized in L&D to distribute materials internally. At the same time, other HR tools are employed to handle budgets and training approvals.
Compensation professionals frequently employ a payroll system, and there are also digital technologies that allow for successful succession planning.
All of these functions are frequently performed in a single system – the HRIS. However, the management of these functionalities is sometimes split up into multiple HR systems.
7. HR data and analytics

The final of the HR essentials is data and analytics. HR has taken a significant step toward being more data-driven in the previous half-decade.
The Human Resource Information Systems that we just mentioned are essentially data entry systems. These platforms’ data can be used to make better, more rational decisions.
HR metrics or HR KPIs are an easy way to keep track of essential data. These are precise measurements that indicate how a company is performing on a given metric. This is known as human resource reporting.
This reporting focuses on the organization’s current and historical state. HR analytics can also be used to create forecasts. Examples include workforce requirements, employee turnover intentions, and the effect of (recruitment) candidate experience on customer satisfaction, among many others.
HR can make more data-driven decisions by actively tracking and analyzing this data. These decisions are frequently more objective, making it easier to gain management support for them.

























