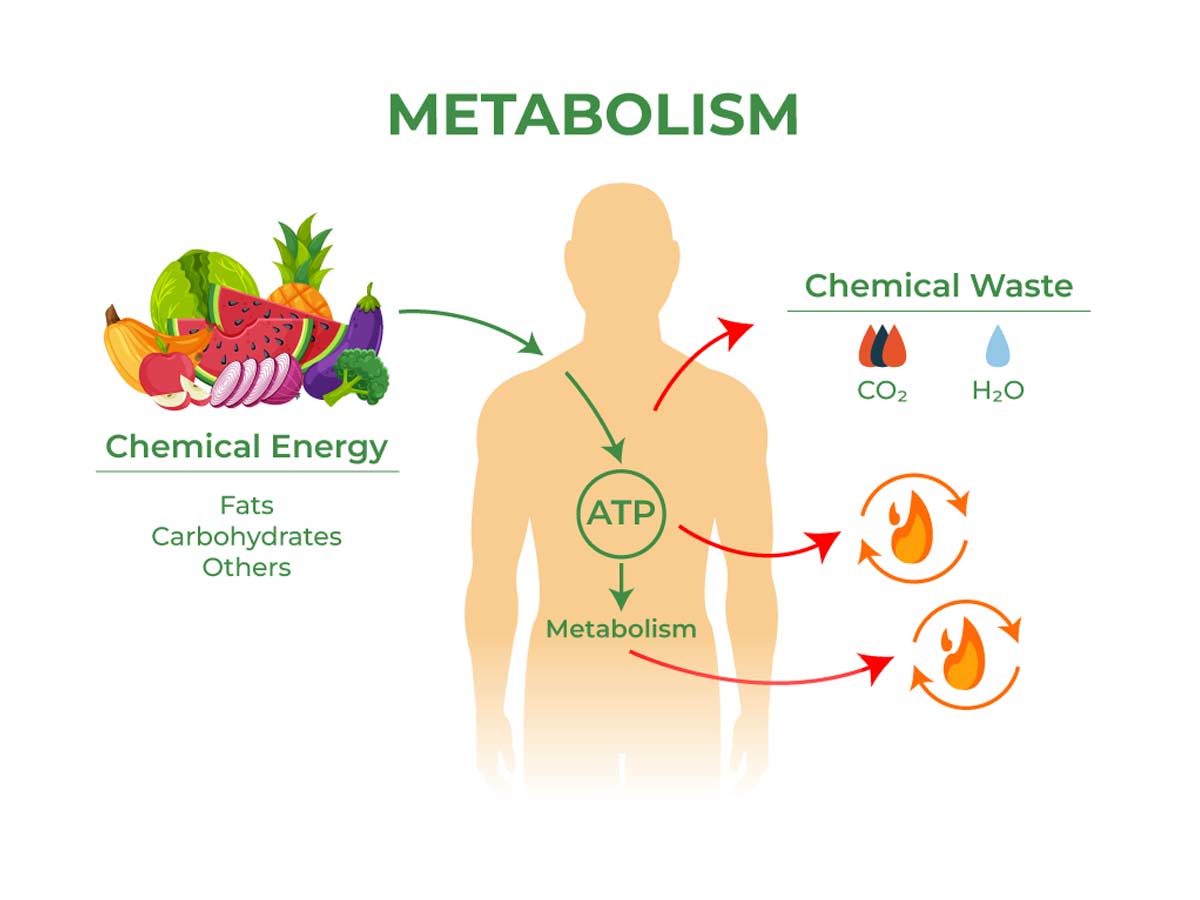
We often blame our metabolisms for problems. We frequently use the word “metabolism” in our irritated chats with girlfriends.
Our inability to consume large amounts of chocolate without gaining weight? Metabolism. The seven extra pounds just won’t go away. Metabolism. our overall exhaustion? Metabolism.
But do you even understand what your metabolism is and how it works?
Eat a Breakfast to Boost Metabolism
Whether eating like a king for breakfast, a prince for lunch, and a pauper for dinner is the key to losing weight is a topic of discussion.
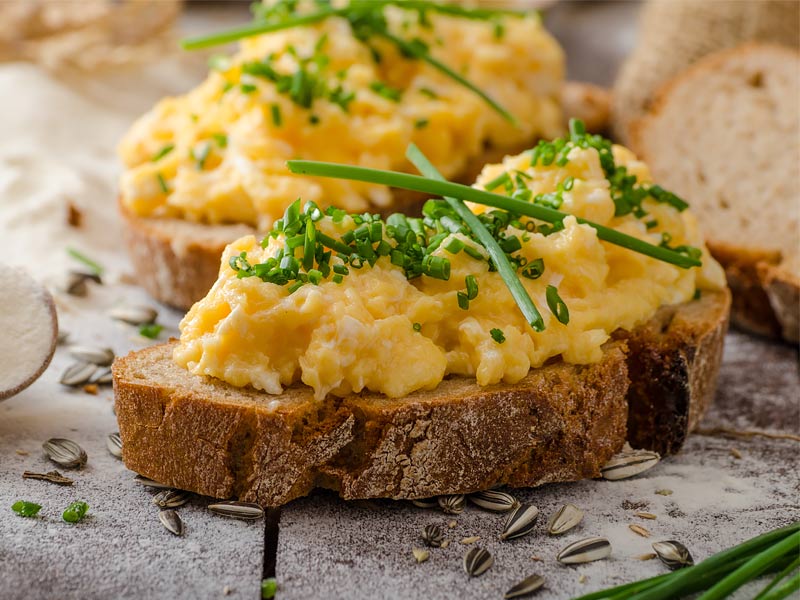

The type of items you add to your breakfast plate actually has an impact on metabolism, so don’t worry too much about size. A 2011 study discovered that you should include low-GL (thus low-sugar) and high-protein foods at breakfast if you want to wake up your system.
Consider something savory and add some lean protein, such as eggs or chicken (yes, for breakfast).
Perform cardio
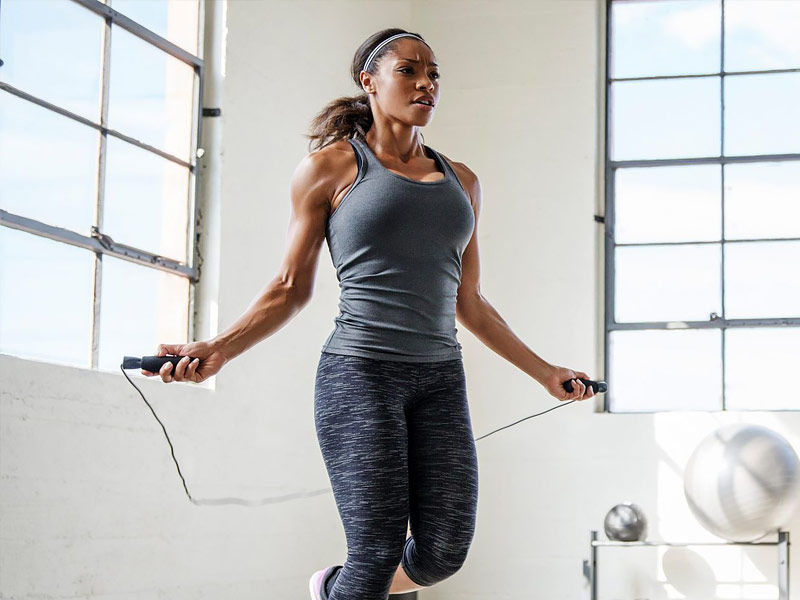

HIIT and heavy lifting will keep your metabolism raised for hours afterward, increasing the burning of fat for far longer than when you were working out. Basic cardio (HIIT excluded) simply increases your calorie burn when engaged.
Consume green tea
“Coffee beans are difficult to crack. Your daily coffee has a lot of antioxidants, but it has also been linked to adrenal exhaustion and too much cortisol, according to health coach Kelly LeVeque. On the other side, drinking brewed green tea is a good method to receive caffeine and provide your body with EGCG, a compound that has been shown to speed metabolism.
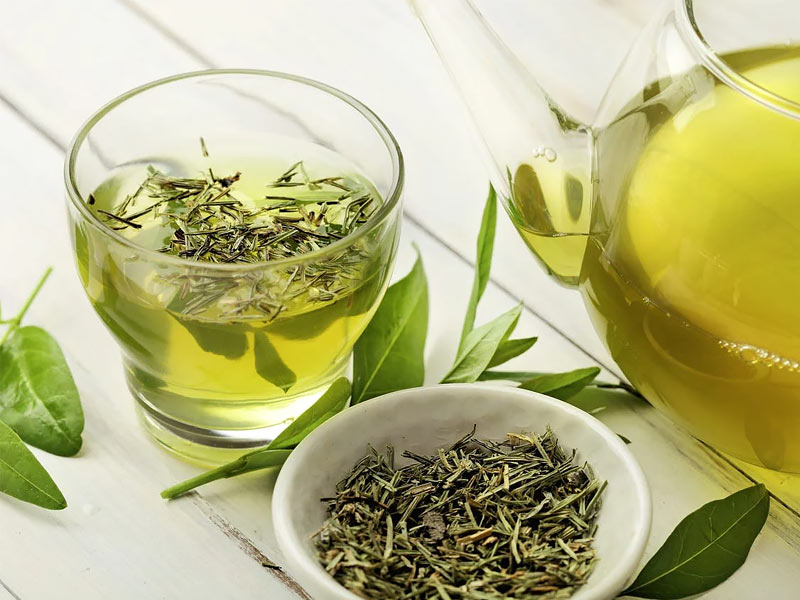

Drink a cup of coffee in the morning, then commit to drinking green tea throughout the afternoon. Avoid all sodas and calorie-dense coffee beverages since high cortisol levels brought on by too much caffeine are more likely to cause you to gain weight around your midsection.
Also, Read 10 Ways for Weight Loss this Summer Season
Consume Micronutrients
Although a healthy metabolism equates to a healthy body, metabolic syndrome can lead to diabetes and heart disease. Of course, exercise and a good diet will help avoid this, but if you’re in a hurry and your workouts and nutritious meals have taken a back seat, make sure you’re supplementing with the necessary micronutrients.
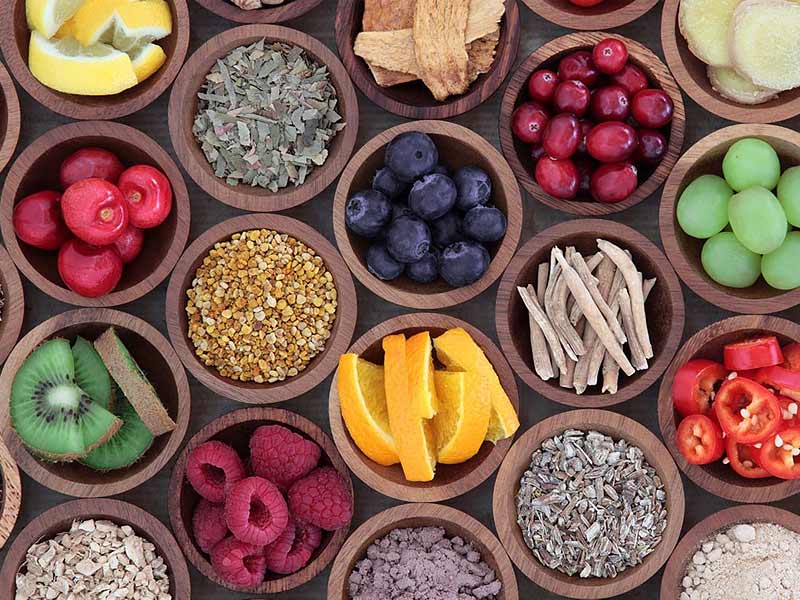

Certain vitamins and minerals have been discovered to help in metabolism. While we may obtain them through a diversified diet, it’s recommended to supplement your intake on occasion. According to research, fat-soluble micronutrients such as vitamins A and E may be important in preventing metabolic syndrome.
Vitamin D may also be important in preventing metabolic syndrome, and because we live in a country where the sun does not constantly shine, it may be worth taking this every day regardless of your diet.
Muscle Growth
As previously stated, strength training is essential for burning more fat at rest (in other words, increasing your BMR). Lean muscle is unquestionably an ally in increasing your BMR. In fact, an earlier study from 2002 discovered that weight-lifting increased calorie burn for 38 hours following exercise.
Su-Nui Escobar, a dietician, observes that “muscle burns more calories than fat at rest.” Muscle atrophy is caused by a lack of activity and occurs naturally as people age.”
Increase Your Sleeping Time
“While sleep does not reduce metabolism, a lack of sleep can cause a hormonal imbalance, resulting in a dysregulation of the hormones associated with hunger and appetite,” Escobar explains.
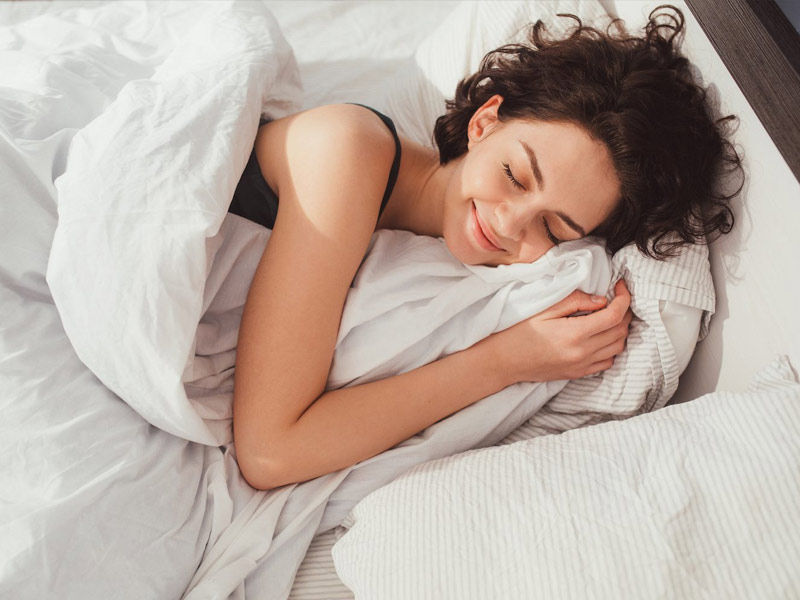

As you can see, lack of sleep does not impair metabolism, but it does make it much more difficult to eat in a way that [leads] to a healthy body weight.”
Hydrate

According to studies, people who drink more water tend to expend more calories. The U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine advise adult men to consume approximately 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) of fluids daily, while adult women should consume approximately 11.5 cups (2.7 liters).