Diagnosis

- Check your knee for swelling, discomfort, warmth, tenderness, and obvious bruising.
- Test your ability to move your lower leg in various directions.
- To assess the structural integrity of your knee, push or pull on the joint.
Imaging tests
In some circumstances, your doctor might advise testing like:
X-ray
An X-ray, which can aid in the early detection of bone fractures and degenerative joint disease, maybe the first test your doctor advises.
CT scan for computerized tomography
Cross-sectional images of the inside of your body are produced by CT scanners by combining X-rays taken at various angles. CT scans can be used to diagnose fractures and abnormalities in the bones. Even when the joint is not inflamed, a specialized CT scan can reliably detect gout.
Ultrasound
This technique creates real-time photographs of the soft tissue structures inside and around your knee using sound waves. During the ultrasound, your doctor might want to move your knee into various positions to look for particular issues.
(MRI) Magnetic resonance imaging
An MRI creates 3D images of the interior of your knee using radio waves and a powerful magnet. This test is extremely useful for identifying damage to soft tissues such as ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and even muscles.
Laboratory tests
If your doctor detects an infection or inflammation, you’ll likely be given blood tests and, in some cases, arthrocentesis, which involves removing a small amount of fluid from within the knee joint with a needle and sending it to a laboratory for analysis.
Treatment
The cause of your knee soreness will determine the best course of treatment.
Medications
To treat conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout that are causing your knee discomfort, your doctor may recommend painkillers and medications.
Therapy
Training the muscles around your knee will increase its stability. Depending on the cause of your discomfort, your doctor may recommend physical therapy or other sorts of strengthening activities.
If you are physically active or participate in sports, you may require workouts to address movement patterns that are causing problems with your knees and to establish proper technique throughout your sport or activity. Exercises to increase flexibility and balance are also beneficial.
Arch supports, often with wedges on one side of the heel, can help redistribute pressure away from the osteoarthritic side of the knee. Different types of braces may be used to protect and support the knee joint in particular circumstances.
Injections
Your doctor may recommend injecting medicines or other things directly into your joint in some circumstances. Here are several examples:
Corticosteroids
Injections of a corticosteroid medicine into your knee joint may help alleviate the symptoms of an arthritis flare and give pain relief that can continue for several months. These injections are not always effective.
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is a viscous fluid that can be injected into your knee to promote mobility and relieve pain. It is similar to the fluid that naturally lubricates joints. Although study results on the effectiveness of this treatment have been inconsistent, alleviation from one or a series of shots may last up to six months.
PRP includes a high concentration of several growth factors, which appear to reduce inflammation and promote healing. PRP may aid some people with osteoarthritis, according to certain studies, but further research is needed.
Also, Read 10 Yoga Poses For PCOS You Can Do At Home
Surgery
If you suffer an injury that may necessitate surgery, you should not have it done right away. Consider the advantages and cons of both nonsurgical rehabilitation and surgical reconstruction by what is most essential to you before making a decision. If you decide to have surgery, you may have the following options:
The procedure is known as arthroscopic surgery
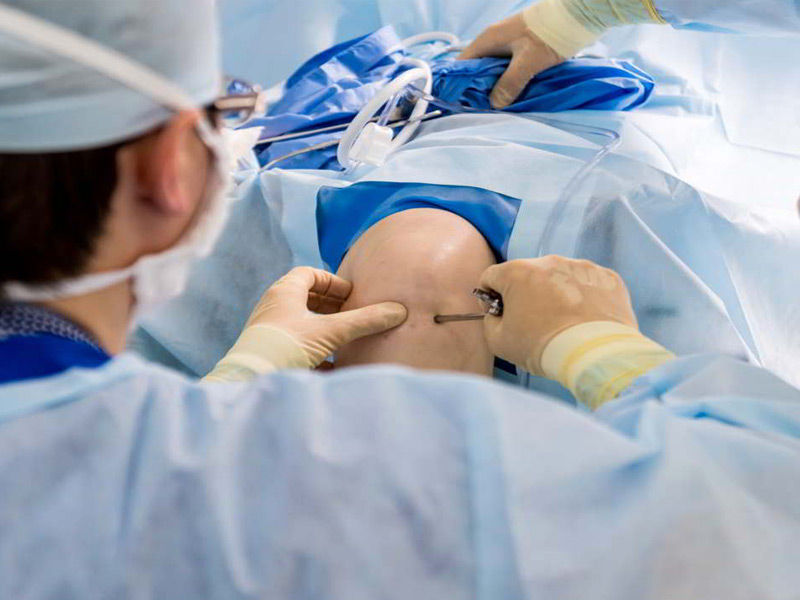
Depending on the severity of your accident, your doctor may be able to inspect and repair joint damage with a fiber-optic camera and long, narrow tools placed through a few small incisions around your knee. Arthroscopy can be performed to remove loose bodies from your knee joint, repair damaged cartilage (particularly if it is causing your knee to lock), & reconstruct torn ligaments.
Surgery for a partial knee replacement
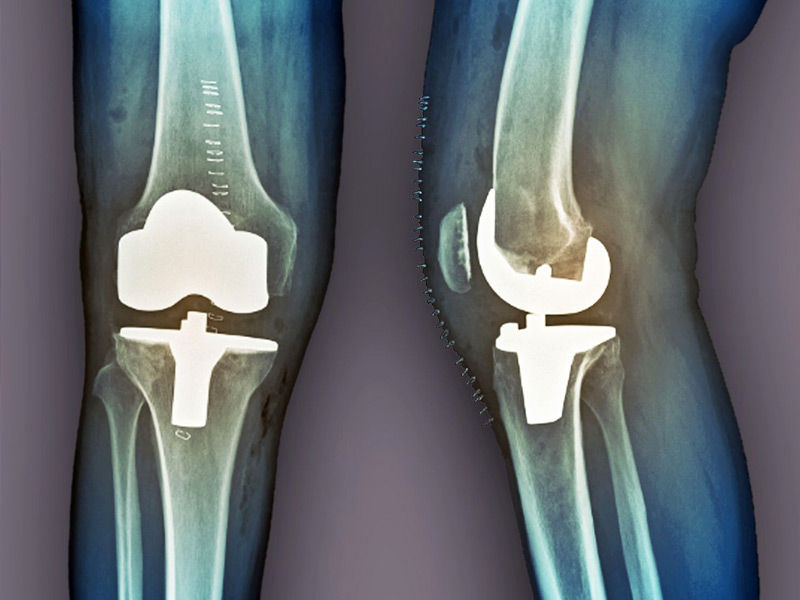
In this treatment, your surgeon replaces only the most damaged area of your knee with metal and plastic components. Because the procedure is typically performed through minor incisions, you should recover faster than if you underwent surgery to replace your entire knee.
Knee replacement surgery
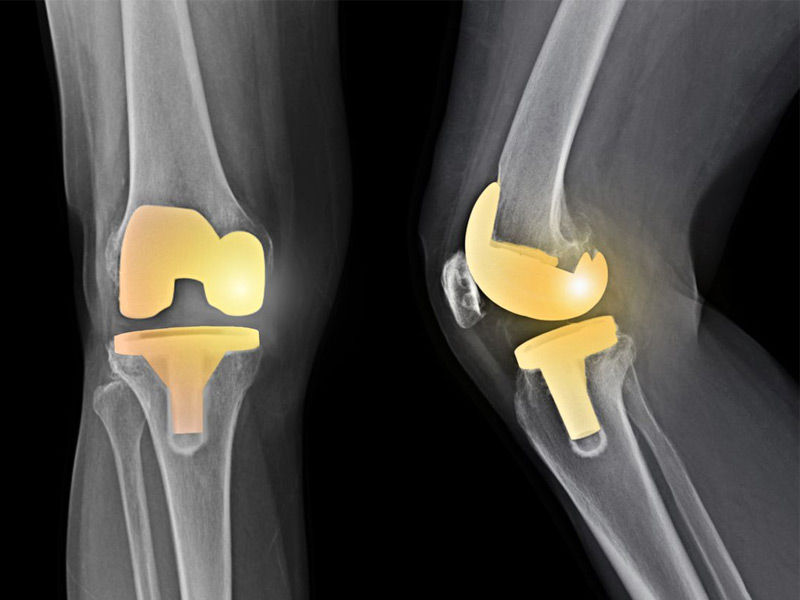
During this procedure, your surgeon will remove the worn-out cartilage and bones from your thighbone, shinbone, & kneecap and replace them with an artificial joint made of metal alloys, premium plastics, and polymers.
Osteotomy
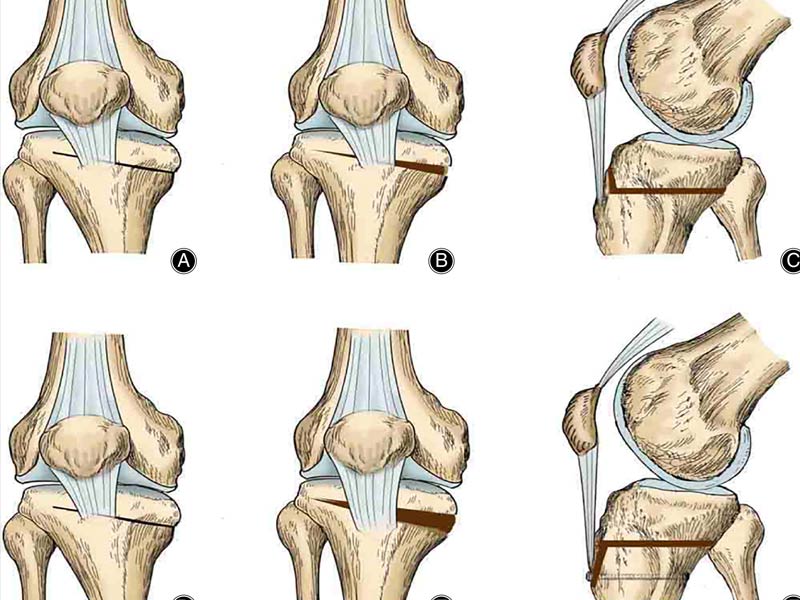
To properly straighten the knee and decrease arthritis discomfort, a bone from the thighbone or shinbone is removed. This procedure may allow you to postpone or avoid total knee replacement surgery.
Home remedies and way of life
Two over-the-counter medications, naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, among others), may ease knee pain.
Some people get comfort by rubbing the injured knee with numbing treatments containing lidocaine or capsaicin, the ingredient that makes chili peppers fiery.
Self-care measures for a knee injury include:
Rest
Give your knee a rest from routine activities to reduce repeated stress injuries, give it time to heal, and help stop further harm. A small injury may only require a day or two of recuperation. Longer recovery times are nearly always required for more serious injuries.
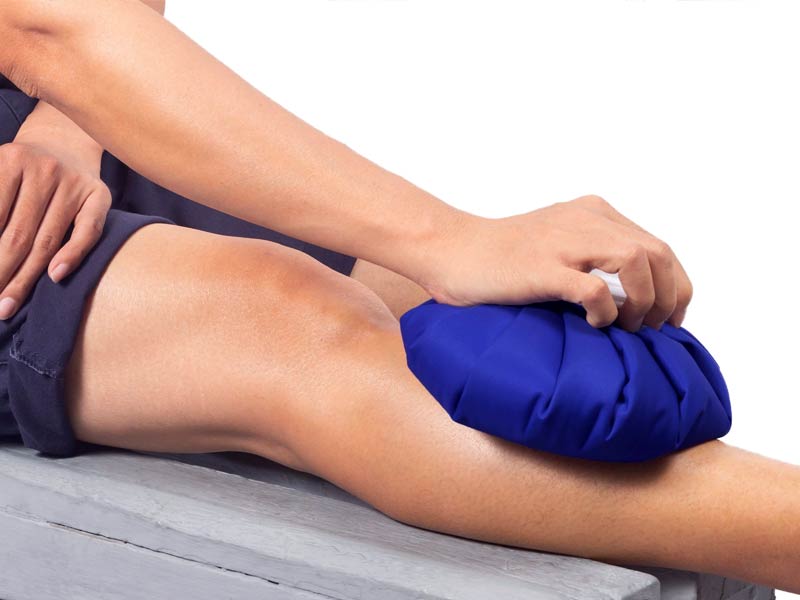
Ice
Ice relieves pain and inflammation. Because it covers the entire knee, a bag of frozen peas works wonderfully. To protect your skin, you can also use an ice pack wrapped in a small towel. Whilst ice therapy is usually effective and secure, it should be limited to a maximum of twenty minutes at a time because of the risk of nerve & skin damage.
Heat
Applying a heat pack or hot water bottle to the troublesome spot on your knee may provide short pain relief.
Compression
This aids in the prevention of fluid buildup in injured tissues while also maintaining knee alignment and stability. Look for a self-adhesive compression bandage that is lightweight and breathable. It should be snug enough to support your knee without restricting circulation.
Elevation
Propping your wounded leg on pillows or resting in a recliner will help minimize swelling.