Although people with conditions like cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy can acquire scoliosis, the majority of infantile scoliosis has an unknown cause. Adolescence is the age bracket where scoliosis, a sideways curvature of the spine, is most frequently diagnosed.
The majority of scoliosis cases are moderate, however, some curvature gets worse as kids get older. Significant scoliosis may be incapacitating. It may be more difficult for the lungs to work correctly if there is less space in the chest as a result of a particularly severe spine bend.
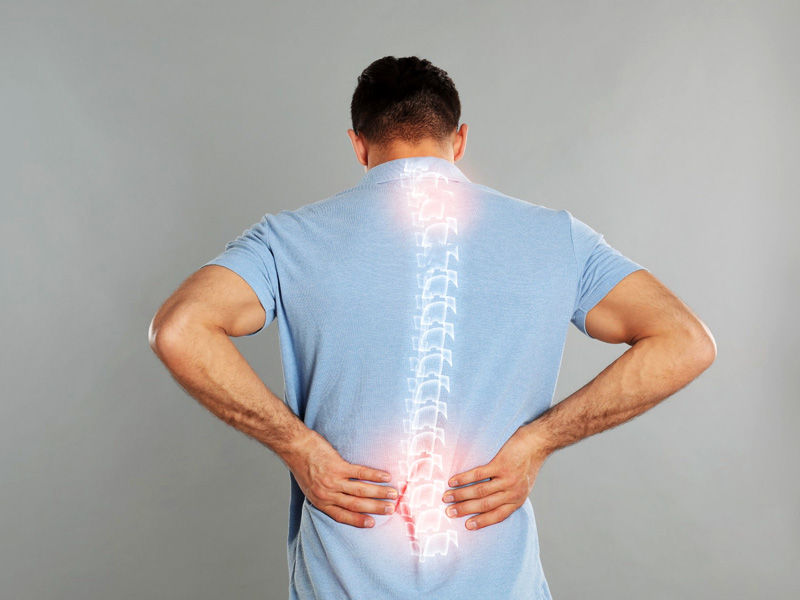
Therapy is not always necessary. To keep the curve from deteriorating, some children will need braces. Others could need surgery to address excessive curvature. Children with mild scoliosis are routinely monitored to see if the curve is getting worse, generally using X-rays.
Symptoms
Scoliosis symptoms and warning signs might include:
- sloping shoulders
- uneven waist one shoulder blade that is more noticeable than the other
- one hip is higher than the other
- one side’s rib cage protruded forward.
- a protrusion on one side of the back when leaning forward

In most cases of scoliosis, the spine will not only curve in one direction but also rotate or twist. As a result, one side of the body’s muscles or ribs protrudes more than the other.
When to seek medical attention
Consult your doctor as soon as possible if your child displays signs of scoliosis. Mild curves may develop without your awareness or your child’s knowledge because they typically don’t hurt and manifest gradually. Sometimes instructors, friends, or fellow athletes notice a child’s scoliosis.
Causes
Although the condition occasionally runs in families, experts think that the most common form of scoliosis may be caused by hereditary factors.
- muscular dystrophy and other specific neuromuscular diseases, such as cerebral palsy
- birth abnormalities that impact how the spine’s bones grow
- previous chest wall surgery as a child
- spine-related injuries or illnesses
- anomalies in the spinal cord
- risk element
The following are risk factors for the most typical type of scoliosis:
Age.
Adolescence is frequently the time when signs and symptoms first develop.
Sex.
The prevalence of mild scoliosis in boys and girls is similar, but girls are far more likely to experience deterioration and require treatment family history. While scoliosis can run in families, the majority of affected youngsters do not.
Complications
breathing issues When scoliosis is severe, the rib cage may press against the lungs, making breathing more challenging.
Back issues. Especially if their aberrant curves are significant and untreated, individuals who experienced scoliosis as children may be more likely to experience chronic back discomfort.
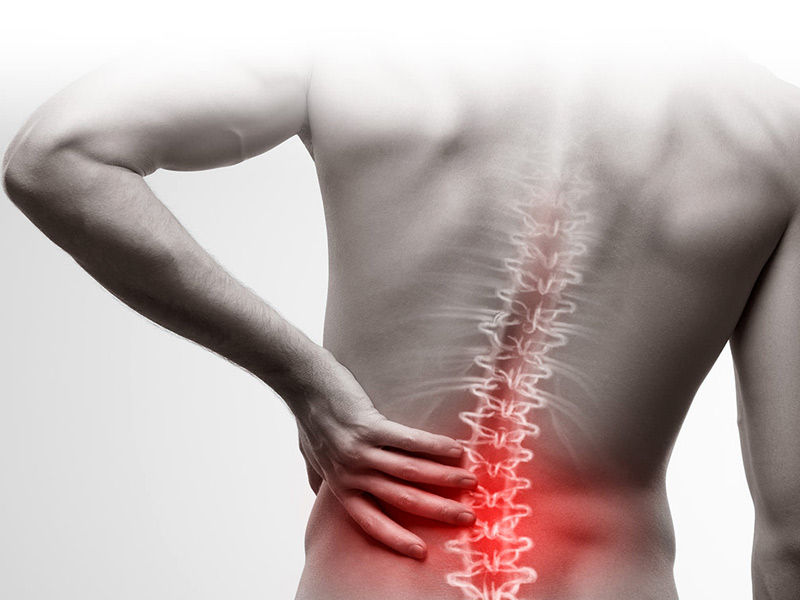
Appearance. Scoliosis can lead to increasingly obvious abnormalities as it progresses, such as lopsided hips and shoulders, protruding ribs, and a tilting of the waist and trunk to one side. Scoliosis sufferers frequently feel self-conscious about their appearance.
Adult-onset or adult-diagnosed scoliosis differs from childhood-onset scoliosis because the underlying causes and therapeutic objectives are different in patients who have already reached skeletal maturity. The majority of scoliosis-affected adults fall into one of the following categories:

1. Adult scoliosis patients who underwent surgical therapy as teens.
2. Adults who did not undergo treatment when they were younger.
3. Adults with a kind of scoliosis known as degenerative scoliosis.
A progression was reported by 40% of adult scoliosis patients in a 20-year study. Of those, 10% demonstrated a very noticeable progression, and the remaining 30% underwent a very minor progression, typically averaging less than one degree per year.
People over the age of 65 are more frequently affected by degenerative scoliosis, which most typically affects the lower back and the lumbar spine. Spinal stenosis, or a narrowing of the spinal canal, which squeezes the spinal nerves and impairs their ability to function correctly, is frequently present.
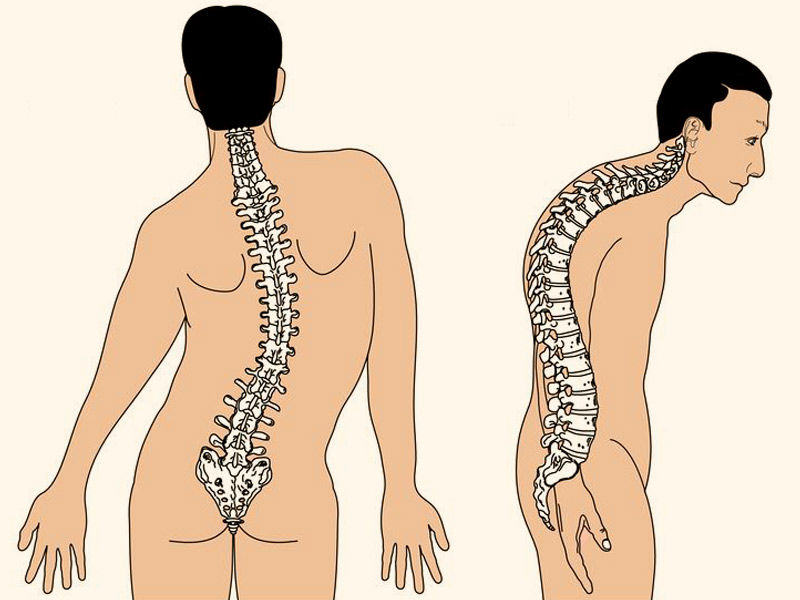
Degenerative scoliosis-related back pain typically develops gradually and is correlated with activity. When conservative measures fail to relieve the pain caused by the condition, surgery may be indicated because the curvature of the spine in this type of scoliosis is frequently only mild.

























