You are already familiar with hard work, whether you’re a professional competitor or have a career that needs you to be on the move. Repetitive and consistent practices are required for many occupations and hobbies.
It’s easy to overdo it, though. This will fatigue the body and mind, which can lead to overexertion.
Overexerting yourself will lead to irritation, pain, or even injury. That’s why it’s essential to listen to your body and be aware of your boundaries.
The good news is that you can shield yourself from unnecessary exertion. We’ll discuss the causes and effects of overexertion in this post, plus tips to prevent it.
What is overexertion?

If you drive yourself too hard, this is known as overexertion. This includes the physical or emotional commitment that is beyond the established expertise.
Overexertion relies on multiple variables, such as yours:
- Age bracket
- medical history
- Ambient or office
- Relevant task or assignment
Because of these variables, at certain times, different persons will become over-exerted. We also have physical and emotional boundaries of our own.
Overexertion can be insecure. It may contribute to severe injuries, such as:
- strains
- sprains
- fractures
In the future, that will even affect your opportunity to continue performing an operation.
What does overexertion cause?

Overexertion is usually related to specific movements or gestures. Let’s look at some of the most important causes of overexertion in more detail.
Repetitive motions
It can lead to hyper-exertion if you repeatedly shift a joint or muscle over a long period. Repeated movements will place pressure on the body, leading to irritation or pain.
Sometimes, repeated gestures are correlated with behaviors such as:
- Using a mouse on a monitor
- Writing or typing
- Working on an assembly line, working
- To kick, strike, or throw a ball
- Training for athletics
- Reproduction of musical instruments
- Knitting or weaving
Inappropriate techniques
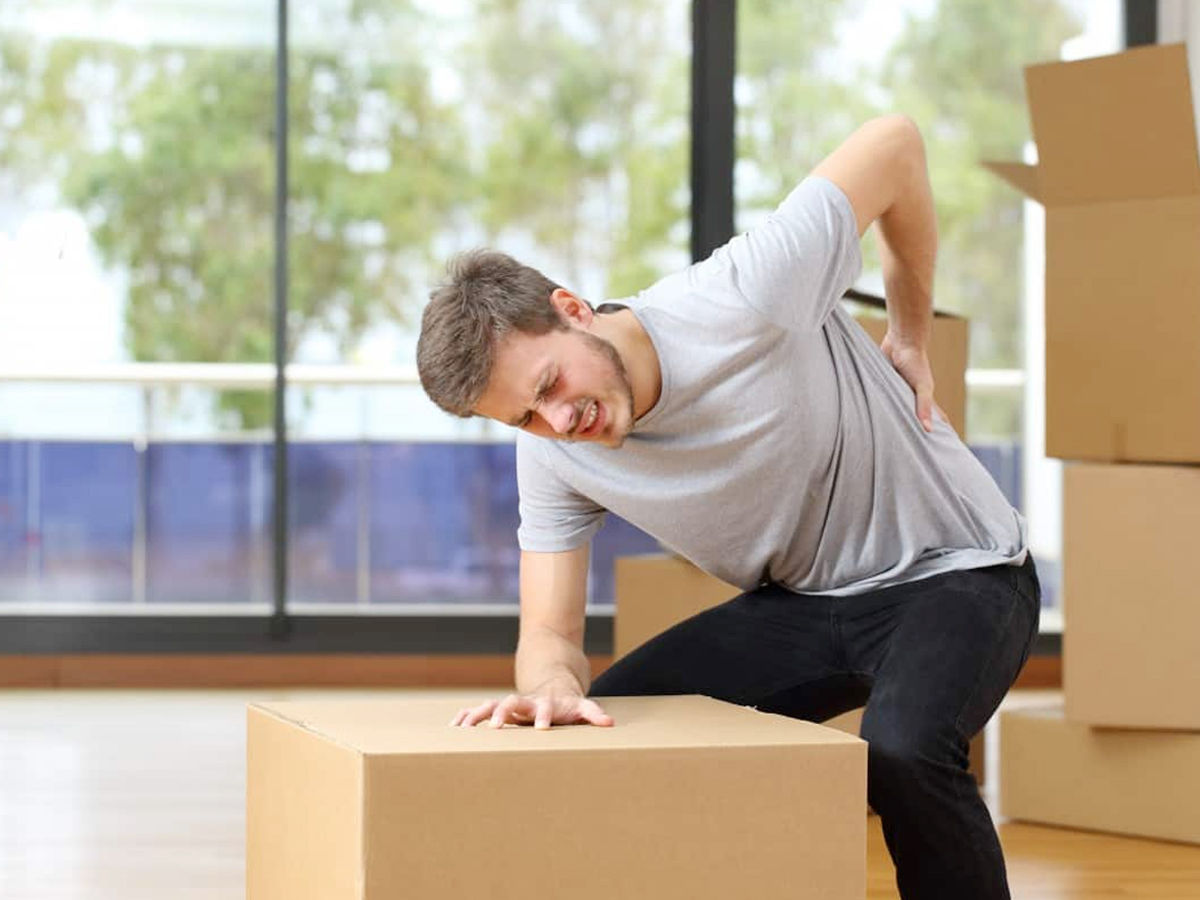
Overexertion can stem from improperly performing an operation or task. This will bring tension to the muscles, bones, joints, and connective tissues and cause overexertion accidents.
Examples of incorrect techniques include:
- Wrongly lifting objects
- Sitting back for a weak stance
- Standing in embarrassing places
- During a workout, using the incorrect type
- When kneeling, not wearing knee pads
- Using the wrong gear or machines
Sudden motions of the body
Overexertion can also be caused by a rapid, forceful motion. If the strategy is wrong, this is more likely to happen.
Abrupt movements that can lead to accidents caused by over-exertion include:
- twisting
- bending
- Thrusting
- pulling
- throwing
- reaching
Activity protracted
If you do an operation without frequent breaks on an ongoing basis, you will gradually get exhausted. It can be hard on the body to make an excess physical effort.
Prolonged behavior may be correlated with:
- For the benefits of physical fitness, overworking
- A lot of days in a row or without any breaks to perform a task or workout
Likewise, after working on a cognitive task for a prolonged time, you will experience mental over-exertion. For example, after several hours of studying or working, you can feel emotionally worn out.
Temperature extremes
An action at high temperatures is another possible source.
Your body must work very hard to maintain its average temperature when it’s really hot or cold. Consequently, you can need to force yourself more challenging to do simple operations, leading to overwork.
Overexertion due to high temperatures is also associated with behaviors such as manual outdoor work and outdoor exercise.
What are the symptoms and signs of overexertion?

You could have the following signs and symptoms if you’ve over-exerted yourself:
The Pain
A typical symptom of you overexerting yourself is pain. You may be feeling the discomfort that feels sharp or achy. It can also be something of a feeling of heating, tingling, throbbing, or pinching.
If you have discomfort, instantly stop doing the operation. Take a pause and a break. Speak to the doctor whether the pain lasts or gets worse.
Injury overuse
Typically, an overuse injury, or a repetitive strain injury, progresses over time slowly. Such examples of typical accidents from overuse include:
- The Disease of the Carpal Tunnel
- (hairline) cracks under stress
- tennis elbow
- Usual signs of injury from overuse include:
- Uh, pain
- tingling
- Insensitivity
- Rigidity
- Weakness in the region affected
It is likely that when you do a particular thing, you can only experience specific effects.
Usually, you will need to be in contact with a hospital, so they can help you cope with this sort of accident. Repetitive strain damage management also includes:
- Treatment of RICE, which reflects rest, ice, compression, elevation
- Protecting the affected areas with a brace or splint
- Injections of steroids
- Inflammatory and pain relief drugs
- Exercises to improve the region affected
- Changing the approach and eliminating places that over-extend the field affected
Tiredness
Tiredness is another typical symptom. Depending on the source of overexertion, it may be physical or emotional.
Physical exhaustion symptoms may include:
- “Heavy” muscles, including when performing tasks of low intensity,
- persistent soreness
- Bad physical quality
- Slow recovery following a workout
Mental tiredness can cause symptoms such as:
- Fog of the Brain
- Struggle to focus
- Increased stress or depression
- Changes in mood
- Depression
In any case, for long periods, stop pushing yourself to work.
Enable yourself to relax and reflect on positive lifestyle habits, such as:
- Eating snacks and nutritious meals
- Doing soft fitness types
- To keep hydrated
- Have decent quality sleep
Also Read, 7 Ways You Can Keep Yourself Fit During The Winters
Increased wounds or diseases
During strenuous workouts, overexertion makes it impossible for the body to recover. Similarly, it will damage your immune system, leaving you more vulnerable to disease.
It might be time to take an emotional or physical break from what you’ve been doing if you keep being hurt or sick. Again, it will help the body recover by eating well and having enough sleep.
Trouble breathing
Try will the speed of the movement if you are unable to breathe during a vigorous exercise.
To ensure the body and brain get the oxygen they need, stop holding your breath, and breathe deeply. Slow breathing will allow the body to calm as well.
How to prevent overexertion
When studying or performing athletic exercises, there are ways to reduce physical over-exertion.
To avoid physical burnout and injury, follow these tips:
- Before doing an operation, stretch and warm up the muscles.
- Take breaks every 30 minutes, mostly if you usually stay for several hours in the same place.
- To keep your knees safe, do workouts, like wrist exercises.
- For the activity or workout you are performing, practice the right technique and shape. If you do not know what the proper form is, inquire for guidance.
- On your knees, lift large things, not your back. Before lifting any bulky objects, bend your legs, and keep the items hidden close to your body.
- Avoid overexercising to shake up the schedule.
- Aim to incorporate in your workout schedule at least 1 day of rest every week.
- For physical exercise, don’t want to do too much too fast. Increase exercise time, duration, and frequency steadily.
- Rest during events that are frequent or strenuous.
You should take some steps to help you cope, whether you feel emotionally drained or stressed by work, childcare, or everyday stressors. Such possibilities include:
- Aim to lighten the load. Seek opportunities to assign assignments and duties to others. Enlist the support of individuals who will assist you with tasks such as childcare, running errands, or caring for loved ones.
- Grab a rest. For a few hours, plan a break, a long weekend, or simply empty the calendar and concentrate on doing something that gives you pleasure.
- The workout. A 2013 study analysis found that exercise can be beneficial for the treatment of stress. It also has the potential to safeguard you against specific health issues associated with stress. Even a 20-minute brisk walk will boost your mood, help you feel more comfortable, and have benefits for mental health.
- Try methods for relaxing. Find time in the day to try to perform a strategy that has been shown to reduce stress levels, even though it’s only 10 to 15 minutes. Meditation, yoga, tai chi, breathing exercises, and total muscle relaxation are some alternatives.
- Give your sleep priority. For mental, emotional, and physical well-being, sleep is essential. Make sure you have at least 7 to 8 hours of sleep every night.
- Keep a Log of Thanks. Using a diary and remind yourself of the many things you’re grateful for, instead of the hard stuff, will help you concentrate on the good aspects of your life.
- Look at medical rehabilitation. To help you deal with emotional fatigue and stress, a mental health provider or psychiatrist will provide you with tools.
The simple truth
Overexertion is typically activated by rapid gestures, abrupt movements, or excessive effort. It can also be correlated with incorrect procedures or running at high temperatures. You can cause fatigue, discomfort or become more vulnerable to injury if you’re overworked.
Overexertion isn’t physical either. When you work too hard or get exhausted by too many responsibilities and obstacles, you will even over-exert yourself physically.
It should be remembered that unnecessary exertion does not mean that you are frail or unable to do so. Instead, it’s a symptom of the need for the body or mind to relax. Take frequent rests, do not overdo anything, and pay attention to the body’s warning signals to prevent excessive exertion.